作者|Ayisha D
编译|VK
来源|Towards Data Science
这篇文章中,我们探讨从语音数据中提取的特征,以及基于这些特征构建模型的不同方法。
语音数字(Spoken digits)数据集是Tensorflow语音数据集的一个子集,它包括数字0-9之外的其他录音。在这里,我们只关注识别口语数字。
数据集可以按如下方式下载。
data = download_url("http://download.tensorflow.org/data/speech_commands_v0.01.tar.gz", "/content/")
with tarfile.open('/content/speech_commands_v0.01.tar.gz', 'r:gz') as tar:
tar.extractall(path='./data')Downloading http://download.tensorflow.org/data/speech_commands_v0.01.tar.gz to /content/speech_commands_v0.01.tar.gz
HBox(children=(FloatProgress(value=1.0, bar_style='info', max=1.0), HTML(value='')))digit = ['zero', 'one', 'two', 'three', 'four', 'five', 'six', 'seven', 'eight', 'nine']
for x in digit:
print(x, ": ", len(os.listdir('/content/data/'+x)))
#平衡zero : 2376
one : 2370
two : 2373
three : 2356
four : 2372
five : 2357
six : 2369
seven : 2377
eight : 2352
nine : 2364评估指标
数字相当平衡,每个类有大约2300个样本。因此,准确度是评估模型性能的一个很好的指标。准确度是正确预测数与总预测数的比较。
对于不平衡的数据集,这不是一个很好的性能度量,因为少数类可能会黯然失色。
循环学习率
在训练一个模型时,学习率逐渐降低,以对训练进行微调。为了提高学习效率,可以采用循环学习率。在这里,学习率在不同时期的最小值和最大值之间波动,而不是单调下降。
初始训练率对模型的性能至关重要,低训练率可防止在训练开始时被卡住,随后的波动抑制了局部极小值的情况。
该项目有三种分类方法:
-
使用五个提取的特征进行Logistic回归分析,准确率为76.19%。
-
仅使用MFCCs的Logistic回归-准确率为95.56%。
-
CNN使用Mel谱图-准确率为95.81%。
通过改变epoch和训练率对模型进行反复训练。隐藏层的数量和每个层中的节点也各不相同。这里描述了每种方法的最佳架构和超参数。由于训练和验证集划分的随机性,再训练的精确度可能略有不同。
项目的源代码在这里:https://github.com/AyishaR/Spokendigit
有五个.ipynb文件:
-
特征提取-提取三种方法所需的CSV文件和特征。
-
特征可视化-在每个类中绘制特征图。
-
Spokendigit五个特征-使用五个提取的特征实现逻辑回归。
-
Spokendigit MFFC-使用MFCC实现逻辑回归。
-
Spokendigit CNN-使用Mel谱图实现CNN。
1.使用五个提取特征的Logistic回归
特征
提取的特征包括:
- Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCCs)-根据人类听觉系统的响应(Mel尺度)间隔的频带组成声音的频谱表示的系数。
- Chroma -与12个不同的音高等级有关。
- Mel spectrogram的平均值-基于Mel标度的Mel谱图。
- Spectral Contrast-表示谱的质心。
- Tonnetz -代表音调空间。
这些特征是大小为(20,)(12,)(128,)(7,)和(6,)的NumPy数组。这些连接起来形成一个大小为(173,)的特征数组。标签被附加到数组的头部,并写入每个记录的CSV文件中。
def extract_features(files):
data, sr = librosa.load('/content/data/'+files.File)
mfccs = np.mean(librosa.feature.mfcc(y = data, sr=sr).T, axis = 0)
stft = np.abs(librosa.stft(data))
chroma = np.mean(librosa.feature.chroma_stft(S = stft, sr = sr).T, axis = 0)
mel = np.mean(librosa.feature.melspectrogram(data, sr).T, axis = 0)
contrast = np.mean(librosa.feature.spectral_contrast(S = stft, sr = sr).T, axis = 0)
tonnetz = np.mean(librosa.feature.tonnetz(y = librosa.effects.harmonic(data), sr = sr).T, axis = 0)
#print(mfccs.shape, stft.shape, chroma.shape, mel.shape, contrast.shape, tonnetz.shape)
row = np.concatenate((mfccs, chroma, mel, contrast, tonnetz), axis = 0).astype('float32')
csvwriter.writerow(np.concatenate(([digit.index(files.Label)], row)))模型
线性回归模型共有1个输入层、2个隐藏层和1个带ReLu激活的输出层。
class SpokenDigitModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.l1 = nn.Linear(173, 1024)
self.l2 = nn.Linear(1024, 512)
self.l3 = nn.Linear(512, 64)
self.l4 = nn.Linear(64, 10)
def forward(self, x):
x = F.relu(self.l1(x))
x = F.relu(self.l2(x))
x = F.relu(self.l3(x))
x = self.l4(x)
return x
def training_step(self, batch):
inputs, labels = batch
outputs = self(inputs)
loss = F.cross_entropy(outputs, labels)
return loss
def validation_step(self, batch):
inputs, labels = batch
outputs = self(inputs)
loss = F.cross_entropy(outputs, labels)
_, pred = torch.max(outputs, 1)
accuracy = torch.tensor(torch.sum(pred==labels).item()/len(pred))
return [loss.detach(), accuracy.detach()] 训练
model = to_device(SpokenDigitModel(), device)
history = []
evaluate(model, val_dl){'accuracy': 0.10285229980945587, 'loss': 3.1926627159118652}history.append(fit(model, train_dl, val_dl, 64, 0.01))r = evaluate(model, val_dl)
yp, yt = predict_dl(model, val_dl)
print("Loss: ", r['loss'], "\nAccuracy: ", r['accuracy'], "\nF-score: ", f1_score(yt, yp, average='micro'))Loss: 2.0203850269317627
Accuracy: 0.7619398832321167
F-score: 0.7586644125105664该模型在CPU上训练约3分钟,准确率为76.19%。
plot(losses, 'Losses')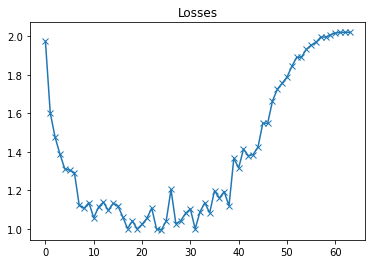
从最小值开始,最终验证损失慢慢变大。
plot(accuracies, 'Accuracy')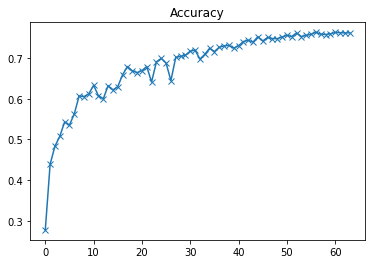
以上为准确率曲线
plot(last_lr, 'Last Learning Rate')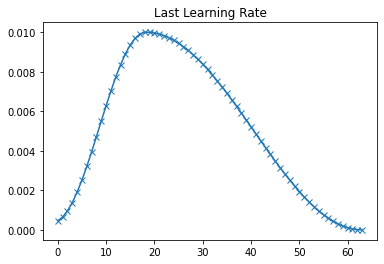
以上为每一epoch的学习率曲线
2.仅使用MFCCs的Logistic回归
特征
该模型仅使用Mel频率倒谱系数(MFCCs)。这个特征是一个大小为(20,)的NumPy数组。它从包含上述所有特征的CSV文件中检索。
模型
线性回归模型共有1个输入层、2个隐藏层和1个带ReLu激活的输出层。
class SpokenDigitModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.l1 = nn.Linear(20, 1024)
self.l2 = nn.Linear(1024, 512)
self.l3 = nn.Linear(512, 64)
self.l4 = nn.Linear(64, 10)
def forward(self, x):
x = F.relu(self.l1(x))
x = F.relu(self.l2(x))
x = F.relu(self.l3(x))
x = self.l4(x)
return x
def training_step(self, batch):
inputs, labels = batch
outputs = self(inputs)
loss = F.cross_entropy(outputs, labels)
return loss
def validation_step(self, batch):
inputs, labels = batch
outputs = self(inputs)
loss = F.cross_entropy(outputs, labels)
_, pred = torch.max(outputs, 1)
accuracy = torch.tensor(torch.sum(pred==labels).item()/len(pred))
return [loss.detach(), accuracy.detach()] 训练
model = to_device(SpokenDigitModel(), device)
history = []
evaluate(model, val_dl){'accuracy': 0.08834186941385269, 'loss': 8.290132522583008}history.append(fit(model, train_dl, val_dl, 128, 0.001))r = evaluate(model, val_dl)
yp, yt = predict_dl(model, val_dl)
print("Loss: ", r['loss'], "\nAccuracy: ", r['accuracy'], "\nF-score: ", f1_score(yt, yp, average='micro'))Loss: 0.29120033979415894
Accuracy: 0.9556179642677307
F-score: 0.9556213017751479该模型在CPU上训练约10分钟,准确率为95.56%。
mfcc是基于Mel尺度的,在Mel尺度中,频率是根据人的听觉反应而不是线性尺度来分组的。人耳是一个经过考验的语音识别系统,因此Mel尺度给出了很好的结果。
另一方面,mfcc容易受到背景噪声的影响,因此在处理干净的语音数据(无噪声或最小噪声)时效果最好。
plot(losses, 'Losses')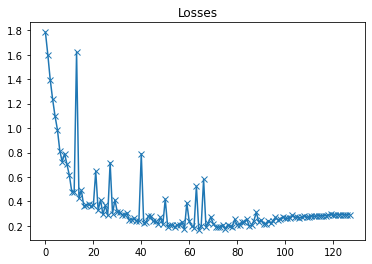
以上是验证集损失曲线
plot(accuracies, 'Accuracy')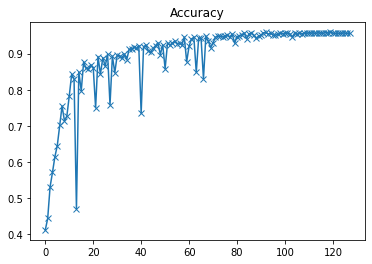
以上是验证集准确率曲线
plot(last_lr, 'Last Learning Rate')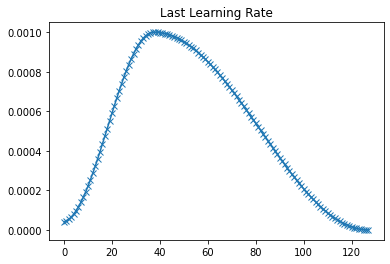
以上是每个epoch最后学习率的曲线
3.使用Mel谱图图像的CNN。
特征
该模型使用了Mel谱图。Mel谱图是将频率转换为Mel标度的谱图。这些特征从录音中提取并存储在驱动器中。这花了4.5个多小时。
def extract_mel(f, label):
data, sr = librosa.load('/content/data/'+label+'/'+f)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=[1,1])
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax.axes.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
ax.axes.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
ax.set_frame_on(False)
S = librosa.feature.melspectrogram(y=data, sr=sr)
librosa.display.specshow(librosa.power_to_db(S, ref=np.max), x_axis='time', y_axis='mel', fmin=50, fmax=280)
file = '/content/drive/My Drive/Dataset/spokendigit/'+label+'/' + str(f[:-4]) + '.jpg'
plt.savefig(file, dpi=500, bbox_inches='tight',pad_inches=0)
plt.close()模型
class SpokenDigitModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.network = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 16, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2),
nn.Conv2d(16, 32, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2),
nn.Conv2d(32, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2),
nn.Conv2d(64, 128, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2),
nn.Conv2d(128, 128, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2),
nn.Conv2d(128, 256, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1),
nn.Flatten(),
nn.Linear(256, 128),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(128, 64),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(64, 10),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.network(x)
def training_step(self, batch):
inputs, labels = batch
outputs = self(inputs)
loss = F.cross_entropy(outputs, labels)
return loss
def validation_step(self, batch):
inputs, labels = batch
outputs = self(inputs)
loss = F.cross_entropy(outputs, labels)
_, pred = torch.max(outputs, 1)
accuracy = torch.tensor(torch.sum(pred==labels).item()/len(pred))
return [loss.detach(), accuracy.detach()] 训练
model = to_device(SpokenDigitModel(), device)
history = []
evaluate(model, val_dl){'accuracy': 0.09851787239313126, 'loss': 2.3029427528381348}history.append(fit(model, train_dl, val_dl, 128, 0.001))r = evaluate(model, val_dl)
yp, yt = predict_dl(model, val_dl)
print("Loss: ", r['loss'], "\nAccuracy: ", r['accuracy'], "\nF-score: ", f1_score(yt, yp, average='micro'))Loss: 1.492598056793213
Accuracy: 0.9581243991851807
F-score: 0.9573119188503804该模型在Colab GPU上训练约5小时,准确率为95.81%。
高准确率可以再次归因于Mel标度。
plot(losses, 'Losses')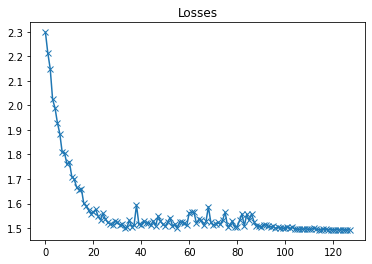
以上是验证集损失曲线
plot(accuracies, 'Accuracy')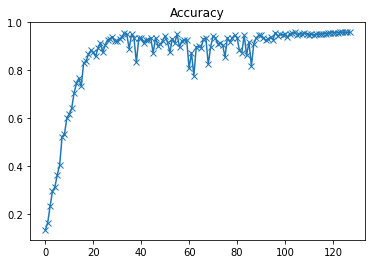
以上是验证集准确度曲线
plot(last_lr, 'Last Learning Rate')
以上是每个epoch最后学习率的曲线
参考
- https://musicinformationretrieval.com/
- [https://github.com/jurgenarias/Portfolio/tree/master/Voice%20Classification/Code](https://github.com/jurgenarias/Portfolio/tree/master/Voice Classification/Code)
- https://arxiv.org/abs/1506.01186
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mel-frequency_cepstrum
原文链接:https://towardsdatascience.com/torch-spoken-digits-recognition-from-features-to-model-357209cd49d1
欢迎关注磐创AI博客站:
http://panchuang.net/
sklearn机器学习中文官方文档:
http://sklearn123.com/
欢迎关注磐创博客资源汇总站:
http://docs.panchuang.net/
原创文章,作者:磐石,如若转载,请注明出处:https://panchuang.net/2020/09/01/torch%ef%bc%9a%e4%bb%8e%e7%89%b9%e5%be%81%e6%8f%90%e5%8f%96%e5%88%b0%e6%a8%a1%e5%9e%8b%e7%9a%84%e8%af%ad%e9%9f%b3%e8%af%86%e5%88%ab/

