在前面的帖子中,我们讨论了以下内容
“最终代码”(The Final Code)
'''
Input functionality
'''
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
data = pd.read_csv('../input/Kannada-MNIST/train.csv')
data = data.sample(frac=1)
#print(int(data.shape[0]/2))
data_first_half = data.head(30000)
data_second_half = data.tail(30000)
### get 100 data points
### making sure that the data is balanced
tmp = pd.DataFrame()
for label in range(10):
if label==0:
tmp = data_first_half[data_first_half['label']==label].head(600)
else:
temp = data_first_half[data_first_half['label']==label].head(600)
tmp = pd.concat([tmp,temp])
data_balanced = tmp
tmp = pd.DataFrame()
for label in range(10):
if label==0:
tmp = data_second_half[data_second_half['label']==label].head(100)
else:
temp = data_second_half[data_second_half['label']==label].head(100)
tmp = pd.concat([tmp,temp])
data_test = tmp2.重塑列车并进行试验
### Convert flattened input train data to image data
data_balanced = data_balanced.sample(frac=1)
data_array = np.zeros((data_balanced.shape[0],1,28,28))
image_data = np.array(data_balanced.drop('label',axis=1))
for i in range(data_balanced.shape[0]):
single_image = image_data[i,:].reshape(1,-1)
single_image = single_image.reshape(-1,28)
data_array[i,0,:,:] = single_image
data_array = data_array/255.
### Convert flattened input test data to image data
data_test = data_test.sample(frac=1)
data_test_input = np.zeros((data_test.shape[0],1,28,28))
image_data = np.array(data_test.drop('label',axis=1))
for i in range(data_test.shape[0]):
single_image = image_data[i,:].reshape(1,-1)
single_image = single_image.reshape(-1,28)
data_test_input[i,0,:,:] = single_image
data_test_input = data_test_input/255.3.对标签进行一次热编码
### Convert Labels to one hot encoding
label = data_balanced['label'].tolist()
one_hot_encoding = np.zeros((data_balanced.shape[0],10))
for i in range(data_balanced.shape[0]):
position = label[i]
one_hot_encoding[i,position] = 14.IM2col1函数定义
def im2col(X,conv1, stride, pad):
"""
Transforms our input image into a matrix.
Parameters:
- X: input image.
- HF: filter height.
- WF: filter width.
- stride: stride value.
- pad: padding value.
Returns:
-cols: output matrix.
"""
# Padding
X_padded = np.pad(X, ((0,0), (0,0), (pad, pad), (pad, pad)), mode='constant')
X = X_padded
new_height = int((X.shape[2]+(2*pad)-(conv1.shape[2]))/stride)+1
new_width = int((X.shape[3]+(2*pad)-(conv1.shape[3]))/stride)+1
im2col_vector = np.zeros((X.shape[1]*conv1.shape[2]*conv1.shape[3],new_width*new_height*X.shape[0]))
c = 0
for position in range(X.shape[0]):
image_position = X[position,:,:,:]
for height in range(0,image_position.shape[1],stride):
image_rectangle = image_position[:,height:height+conv1.shape[2],:]
if image_rectangle.shape[1]
else:
for width in range(0,image_rectangle.shape[2],stride):
image_square = image_rectangle[:,:,width:width+conv1.shape[3]]
if image_square.shape[2]
else:
im2col_vector[:,c:c+1]=image_square.reshape(-1,1)
c = c+1
return(im2col_vector)5.最大池函数
def maxpool_multiple(input_image,stride=2):
input_width = input_image.shape[3]
input_height = input_image.shape[2]
filter_width = 2
filter_height = 2
output_width = int((input_width-filter_width)/stride)+1
output_height = int((input_height-filter_height)/stride)+1
output_image = np.zeros((input_image.shape[0],input_image.shape[1],output_width,output_height))
for i in range(output_image.shape[0]):
output_image[i:i+1,:,:,:] = maxpool(input_image[i:i+1,:,:,:],stride=2)
return output_image
def maxpool(input_image,stride=2):
input_width = input_image.shape[3]
input_height = input_image.shape[2]
filter_width = 2
filter_height = 2
n_channels = input_image.shape[1]
num_images = input_image.shape[0]
output_width = int((input_width-filter_width)/stride)+1
output_height = int((input_height-filter_height)/stride)+1
output = np.zeros((n_channels,output_width*output_height))
c=0
for height in range(0,input_height,stride):
if height+filter_height<=input_height:
image_rectangle = input_image[0,:,height:height+filter_height,:]
for width in range(0,input_width,stride):
if width+filter_width<=input_width:
image_square = image_rectangle[:,:,width:width+filter_width]
image_flatten = image_square.reshape(-1,1)
# print(image_flatten)
# print('----')
output[:,c:c+1] = np.array([float(max(i)) for i in np.split(image_flatten,n_channels)]).reshape(-1,1)
c+=1
final_output = np.array(np.hsplit(output,1)).reshape((1,n_channels,output_height,output_width))
return final_output6.RELU函数、SoftMax函数和存储最大池索引的函数
def ReLU(x):
return (x>0)*x7.重塑错误层以进行反向传播
def error_layer_reshape(error_layer):
test_array = error_layer
test_array_new = np.zeros((test_array.shape[1],test_array.shape[0]*test_array.shape[2]*test_array.shape[3]))
for i in range(test_array_new.shape[0]):
test_array_new[i:i+1,:] = test_array[:,i:i+1,:,:].ravel()
return test_array_new8.培训和测试
'''Simple Architecture for Digit Recognition
1) (1,1,28,28)
2) Convolution filter (2,1,5,5)
3) (Max Pool 2x2)
4) Fc layer (1,288)
5)Second FC (1,60)
6) Output Layer(1,10)
'''
epochs = 50
batch_size = 128
batches = int(data_array.shape[0]/batch_size)
conv1 = np.random.randn(2,1,5,5)*np.sqrt(1./5.)
W1 = np.random.rand(60,288)/np.sqrt(288)
B0 = np.zeros((60,1))/np.sqrt(288)
W2 = np.random.rand(10,60)/np.sqrt(60)
B1 = np.zeros((10,1))/np.sqrt(60)
learning_rate = 0.001
## Implementing Adam Optimizer
beta1 = 0.9
beta2 = 0.995
momentum_w1 = 0
momentum_w2 = 0
momentum_b0 = 0
momentum_b1 = 0
momentum_conv1 = 0
velocity_w1 = 0
velocity_w2 = 0
velocity_b0 = 0
velocity_b1 = 0
velocity_conv1 = 0
for epoch_num in range(epochs):
'''
Choose chunks of data based on batch size
'''
i = 0
permutation = np.random.permutation(data_array.shape[0])
data_array_train = data_array[permutation,:,:,:]
one_hot_encoding_train = one_hot_encoding[permutation,:]
for i in range(batches):
start = i*batch_size
end = min(start+batch_size,data_array.shape[0]-1)
X_batch = data_array_train[start:end,:,:,:]
y_batch = one_hot_encoding_train[start:end,:].T
### First Convolutional Layer
#X_conv = conv2dim2col_multiple(input_image=X_batch,conv_filter=conv1,stride=1)
X_im2col = im2col(X=X_batch,conv1=conv1,stride=1,pad=0)
conv1_reshaped = conv1.reshape(conv1.shape[0],-1)
X_conv = conv1_reshaped@X_im2col
X_conv = np.array(np.hsplit(X_conv,X_batch.shape[0])).reshape((X_batch.shape[0],conv1.shape[0],24,24))
### Pass through ReLU
X_relu = ReLU(X_conv)
### Pass Through Max Pool
X_maxpool = maxpool_multiple(X_relu,stride=2)
### Get the indices of maxpool
max_indices = maxpool_indices_multiple(X_relu,stride=2,filter_height=2, filter_width=2)
### Flatten the maxpool output
input_shape = X_maxpool.shape[0]
num_channels = X_maxpool.shape[1]
input_width = X_maxpool.shape[2]
input_height = X_maxpool.shape[3]
X_maxpool_flatten= np.zeros((input_width*input_height*num_channels,input_shape))
for image in range(input_shape):
X_maxpool_flatten[:,image:image+1] = X_maxpool[image:image+1,:,:,:].ravel().reshape(-1,1)
### Getting into fully connected layers
fc1 = ReLU(W1@X_maxpool_flatten+B0)
final_fc = softmax(W2@fc1+B1)
# print('Sum of Final FC')
# print(np.sum(final_fc))
# print(final_fc)
# break
# print('Loss:')
# print(cross_entropy(y=y_batch,y_hat=final_fc))
### Calculating Loss Through Backprop
delta_2 = (final_fc-y_batch)
delta_1 = np.multiply(W2.T@delta_2,dReLU(W1@X_maxpool_flatten+B0))
delta_0 = np.multiply(W1.T@delta_1,1.0)
dW1 = delta_1@X_maxpool_flatten.T
dW2 = delta_2@fc1.T
dB0 = np.sum(delta_1,axis=1,keepdims=True)
dB1 = np.sum(delta_2,axis=1,keepdims=True)
# print('Delta 2')
# print(delta_2)
### Calculating Error for Last Layer before flattening
delta_maxpool = delta_0.reshape(X_maxpool.shape)
### Calculating Error for previous convolutional layer
delta_conv = np.zeros(X_conv.shape)
for image in range(len(max_indices)):
indices = max_indices[image]
for p in indices:
delta_conv[image:image+1,p[1],p[2],p[3]] = delta_maxpool[image:image+1,p[5],p[6],p[7]]
delta_conv = np.multiply(delta_conv,dReLU(X_conv))
### using Im2col
X_batch_im2col = im2col(X=X_batch,conv1=conv1, stride=1, pad=0)
delta_conv_reshape = error_layer_reshape(delta_conv)
conv1_delta = (delta_conv_reshape@X_batch_im2col.T).reshape(2,1,5,5)
momentum_w1 = beta1*momentum_w1 + ((1-beta1)*dW1)
momentum_w2 = beta1*momentum_w2 + ((1-beta1)*dW2)
momentum_b0 = beta1*momentum_b0 + ((1-beta1)*dB0)
momentum_b1 = beta1*momentum_b1 + ((1-beta1)*dB1)
momentum_conv1 = beta1*momentum_conv1 + ((1-beta1)*conv1_delta)
velocity_w1 = beta2*velocity_w1 + ((1-beta2)*dW1**2)
velocity_w2 = beta2*velocity_w2 + ((1-beta2)*dW2**2)
velocity_b0 = beta2*velocity_b0 + ((1-beta2)*dB0**2)
velocity_b1 = beta2*velocity_b1 + ((1-beta2)*dB1**2)
velocity_conv1 = beta2*velocity_conv1 + ((1-beta2)*conv1_delta**2)
#conv1_delta = conv_filter_error_multiple(input_image=X_batch,error_layer=delta_conv,conv_filter=conv1,stride=1)
#print('conv1 delta done')
## Update Weights
conv1 = conv1 - learning_rate * momentum_conv1/np.sqrt(velocity_conv1+0.0000001)
W1 = W1 - learning_rate*momentum_w1/np.sqrt(velocity_w1+0.0000001)
W2 = W2 - learning_rate*momentum_w2/np.sqrt(velocity_w2+0.0000001)
B0 = B0 - learning_rate*momentum_b0/np.sqrt(velocity_b0+0.0000001)
B1 = B1 - learning_rate*momentum_b1/np.sqrt(velocity_b1+0.0000001)
#print('Back Prop Done!')
#i+=1
X = data_array
y = one_hot_encoding.T
X_im2col = im2col(X=X,conv1=conv1,stride=1,pad=0)
conv1_reshaped = conv1.reshape(conv1.shape[0],-1)
X_conv = conv1_reshaped@X_im2col
X_conv = np.array(np.hsplit(X_conv,X.shape[0])).reshape((X.shape[0],conv1.shape[0],24,24))
### Pass through ReLU
X_relu = ReLU(X_conv)
### Pass Through Max Pool
X_maxpool = maxpool_multiple(X_relu,stride=2)
input_shape = X_maxpool.shape[0]
num_channels = X_maxpool.shape[1]
input_width = X_maxpool.shape[2]
input_height = X_maxpool.shape[3]
X_maxpool_flatten= np.zeros((input_width*input_height*num_channels,input_shape))
for image in range(input_shape):
X_maxpool_flatten[:,image:image+1] = X_maxpool[image:image+1,:,:,:].reshape(-1,1)
### Getting into fully connected layers
fc1 = ReLU(W1@X_maxpool_flatten+B0)
final_fc = softmax(W2@fc1+B1)
#### Test Data
X = data_test_input
#y = one_hot_encoding.T
X_im2col = im2col(X=X,conv1=conv1,stride=1,pad=0)
conv1_reshaped = conv1.reshape(conv1.shape[0],-1)
X_conv = conv1_reshaped@X_im2col
X_conv = np.array(np.hsplit(X_conv,X.shape[0])).reshape((X.shape[0],conv1.shape[0],24,24))
### Pass through ReLU
X_relu = ReLU(X_conv)
### Pass Through Max Pool
X_maxpool = maxpool_multiple(X_relu,stride=2)
input_shape = X_maxpool.shape[0]
num_channels = X_maxpool.shape[1]
input_width = X_maxpool.shape[2]
input_height = X_maxpool.shape[3]
X_maxpool_flatten= np.zeros((input_width*input_height*num_channels,input_shape))
for image in range(input_shape):
X_maxpool_flatten[:,image:image+1] = X_maxpool[image:image+1,:,:,:].reshape(-1,1)
### Getting into fully connected layers
fc1 = ReLU(W1@X_maxpool_flatten+B0)
final_fc_test = softmax(W2@fc1+B1)
if epoch_num % 5 == 0:
### Getting accuracy
print('Epoch :', epoch_num)
labels_predict = np.argmax(final_fc,axis=0)
labels_df = data_balanced[['label']]
labels_predict = labels_predict.tolist()
labels_predict = [int(value) for value in labels_predict]
#labels_df.loc[:,'label_predict'] = labels_predict
labels_df.insert(1,'label_predict',labels_predict)
accuracy = np.sum(labels_df['label']==labels_df['label_predict'])/labels_df.shape[0]
print('Train Accuracy')
print(round(accuracy*100,2),"%")
### Test Accuracy
labels_predict = np.argmax(final_fc_test,axis=0)
labels_df = data_test[['label']]
labels_predict = labels_predict.tolist()
labels_predict = [int(value) for value in labels_predict]
labels_df.insert(1,'label_predict',labels_predict)
#labels_df.loc[:,'label_predict'] = labels_predict
accuracy = np.sum(labels_df['label']==labels_df['label_predict'])/labels_df.shape[0]
print('Test Accuracy')
print(round(accuracy*100,2),"%")
print('-------------------------')
# print(cross_entropy(y=y,y_hat=final_fc))
print('Done!')9.输出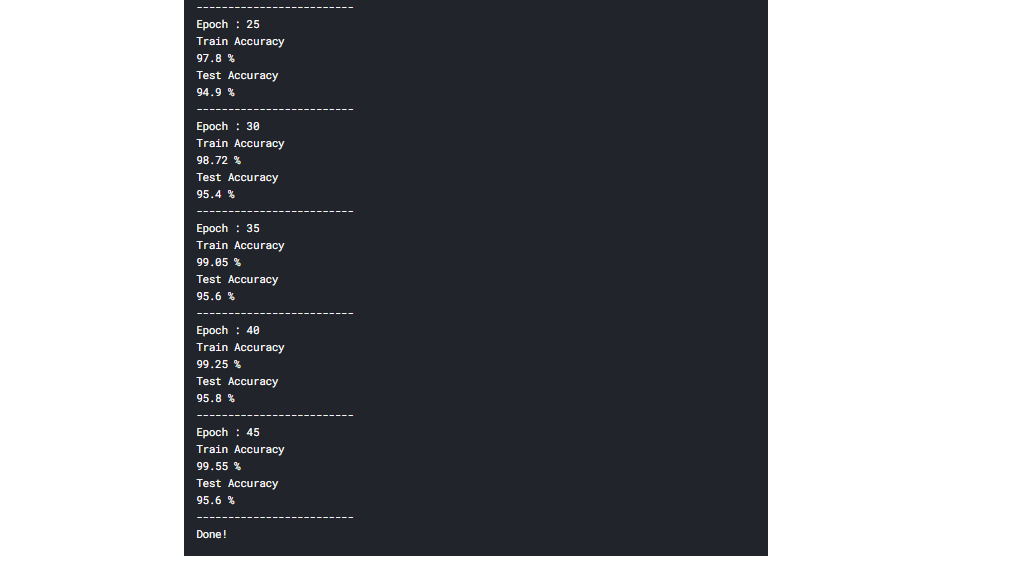
结果
训练正确率达到99%,测试正确率达到95%。代码可以在这里找到。here.
原创文章,作者:fendouai,如若转载,请注明出处:https://panchuang.net/2021/06/21/%e7%ae%80%e5%8d%95%e7%9a%84cnn%e4%bd%bf%e7%94%a8numpy%e7%ac%ac%e5%85%ad%e9%83%a8%e5%88%86%e6%8a%8a%e5%ae%83%e4%bb%ac%e6%94%be%e5%9c%a8%e4%b8%80%e8%b5%b7/

