爬取两万多租房数据,告诉你广州房租现状(4)
精品文章,第一时间送达

转载自:zone7,未经允许不得二次转载
概述
-
前言
-
统计结果
-
爬虫代码实现
-
爬虫分析实现
-
后记
前言
建议在看这篇文章之前,请看完这三篇文章,因为本文是依赖于前三篇文章的:
八月份的时候,由于脑洞大开,决定用 python 爬虫爬取了深圳的租房数据,并写了文章《用Python告诉你深圳房租有多高》,文章得到了一致好评和众多转载。由于我本身的朋友圈大多都在广州、深圳,因此,早就有挺多小伙伴叫我分析一下广州的租房价格现状,这不,文章就这样在众多呼声中出炉了。然后,此次爬虫技术也升级了,完善了更多细节。源码值得细细探究。此次分析采集了广州 11 个区,23339 条数据,如下图:
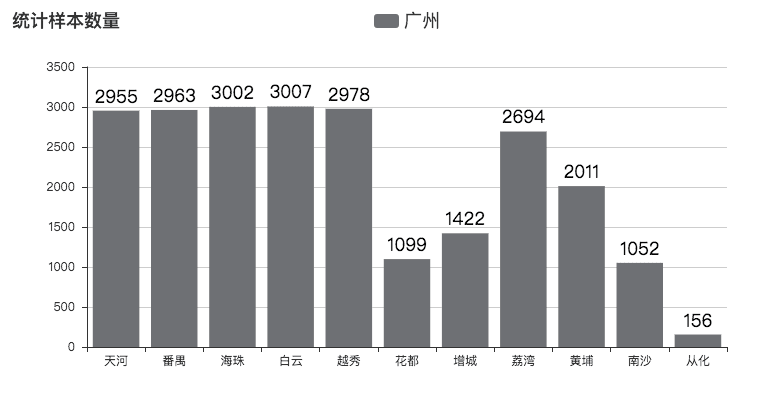
其中后半部分地区数据量偏少,是由于该区房源确实不足。因此,此次调查也并非非常准确,权且当个娱乐项目,供大家观赏。
统计结果
我们且先看统计结果,然后再看技术分析。
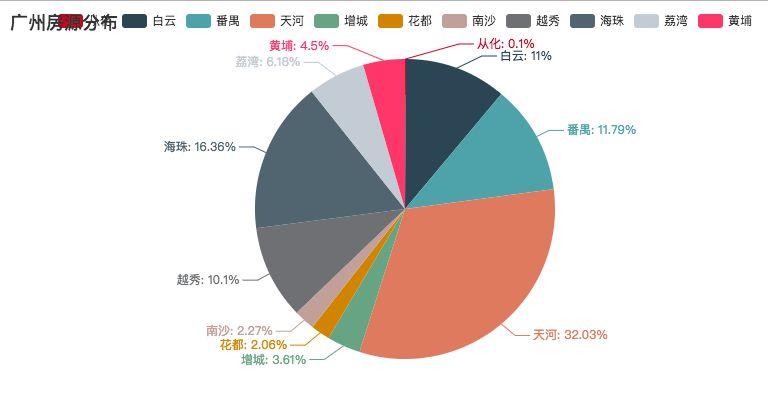
广州房源分布:(按区划分)
其中天河占据了大部分房源。但这块地的房租可是不菲啊。
房租单价:(每月每平方米单价 — 平均数)
即是 1 平方米 1 个月的价格。方块越大,代表价格越高。
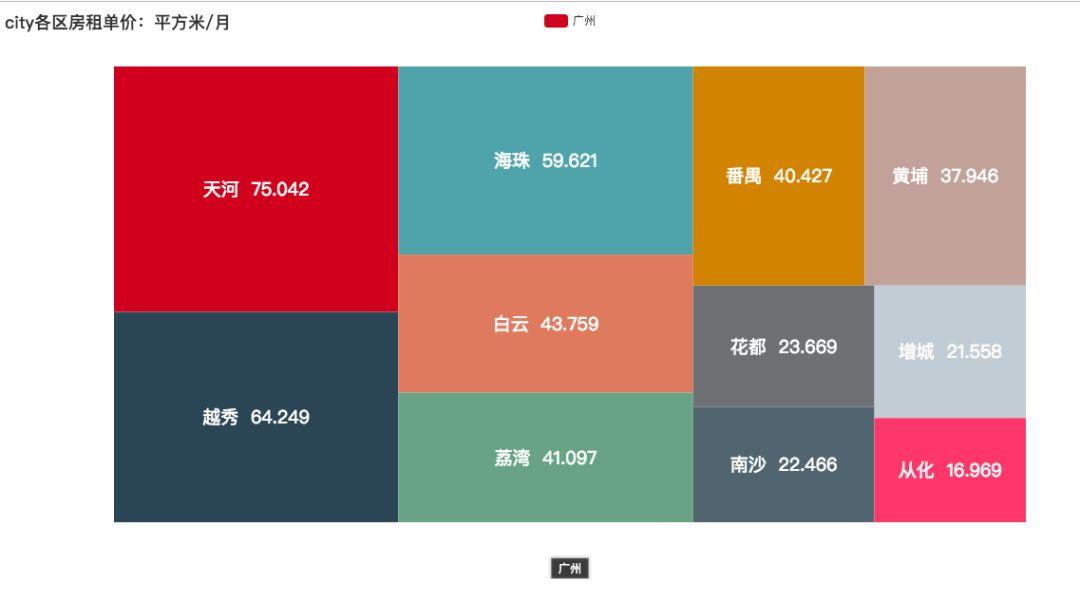
可以看出天河、越秀、海珠都越过了 50 大关,分别是 75.042 、64.249、59.621 ,是其他地区的几倍。如果在天河租个 20 平方的房间:
75.042 x 20 = 1500.84
再来个两百的水电、物业:
1500.84 + 200 = 1700.84
我们按正常生活来算的话,每天早餐 10 块,中午 15 块,晚饭 15 块:
1700.84 + 40 x 30 = 2700.84
那么平时的日常生活需要 2700.84 块。
隔断时间下个馆子,每个月买些衣服,交通费,谈个女朋友,与女朋友出去逛街,妥妥滴加个 2500
2700.84 + 2500 = 5200.84
给爸妈一人一千:
5200.84 + 2000 = 7200.84
月薪一万还是有点存款的,比深圳好一点,但是可能广州的薪资就没深圳那么高了。
房租单价:(每日每平方米单价 — 平均数)
即是 1 平方米 1 天的价格。
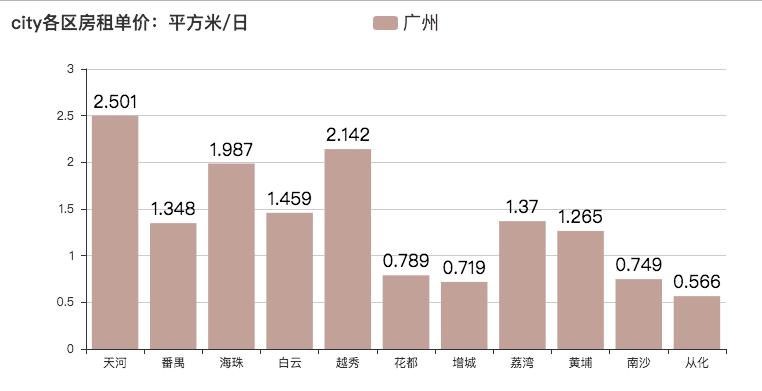
哈哈,感受一下寸土寸金的感觉。[捂脸]

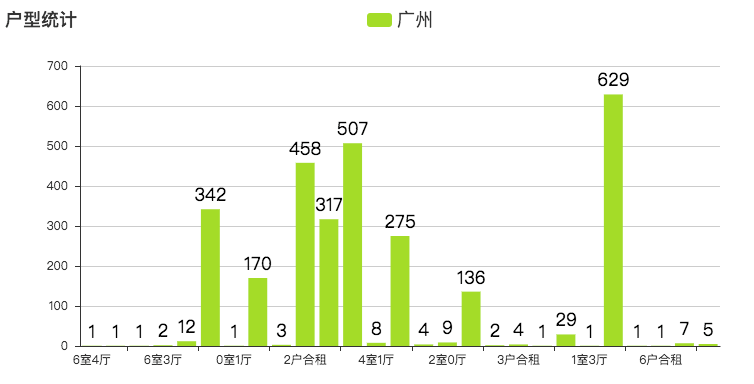
户型
户型主要以 3 室 2 厅与 2 室 2 厅为主。与小伙伴抱团租房是最好的选择了,不然与不认识的人一起合租,可能会发生一系列让你不舒服的事情。字体越大,代表户型数量越多。

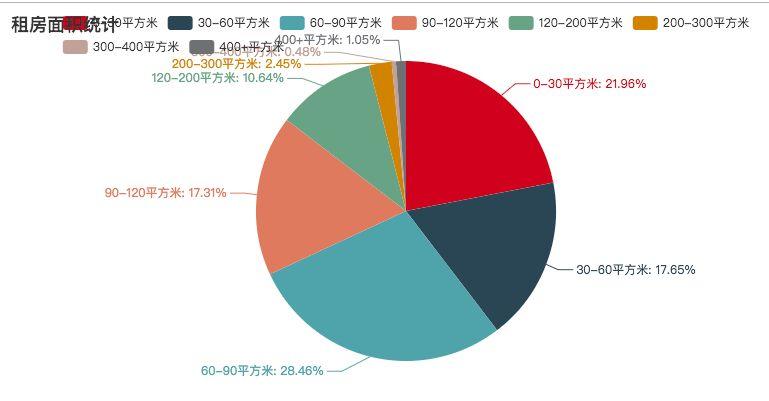
租房面积统计
其中 30 – 90 平方米的租房占大多数,如今之计,也只能是几个小伙伴一起租房,抱团取暖了。
租房描述词云
这是爬取的租房描述,其中字体越大,标识出现的次数越多。其中【住家、全套、豪华、齐全】占据了很大的部分,说明配套设施都是挺齐全的。

爬虫技术分析
-
请求库:scrapy、requests
-
HTML 解析:BeautifulSoup
-
词云:wordcloud
-
数据可视化:pyecharts
-
数据库:MongoDB
-
数据库连接:pymongo
爬虫代码实现
跟上一篇文章不一样,这是使用了 scrapy 爬虫框架来爬取数据,各个方面也进行了优化,例如:自动生成各个页面的地址。
由于房某下各个区域的首页地址和首页以外的地址的形式是不一样的,但是又一定的规律,所以需要拼接各个部分的地址。
首页地址案例:
# 第一页
http://gz.zu.fang.com/house-a073/
非首页地址:
# 第二页
http://gz.zu.fang.com/house-a073/i32/
# 第三页
http://gz.zu.fang.com/house-a073/i33/
# 第四页
http://gz.zu.fang.com/house-a073/i34/

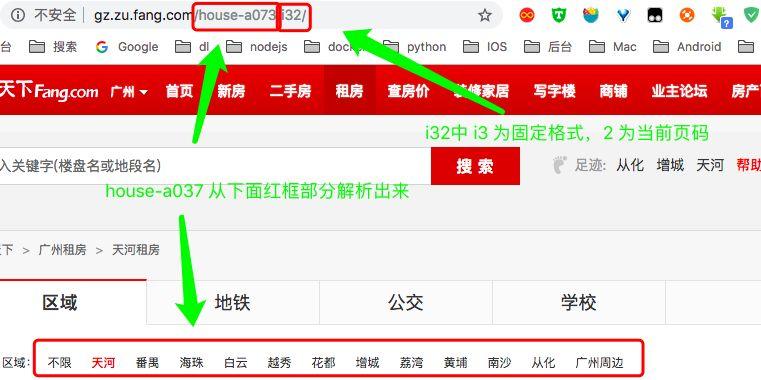
先解析首页 url
def head_url_callback(self, response):
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.body, "html5lib")
dl = soup.find_all("dl", attrs={"id": "rentid_D04_01"}) # 获取各地区的 url 地址的 dl 标签
my_as = dl[0].find_all("a") # 获取 dl 标签中所有的 a 标签,
for my_a in my_as:
if my_a.text == "不限": # 不限地区的,特殊处理
self.headUrlList.append(self.baseUrl)
self.allUrlList.append(self.baseUrl)
continue
if "周边" in my_a.text: # 清除周边地区的数据
continue
# print(my_a["href"])
# print(my_a.text)
self.allUrlList.append(self.baseUrl + my_a["href"])
self.headUrlList.append(self.baseUrl + my_a["href"])
print(self.allUrlList)
url = self.headUrlList.pop(0)
yield Request(url, callback=self.all_url_callback, dont_filter=True)
再解析非首页 url
这里先获取到各个地区一共有多少页,才能拼接具体的页面地址。
# 再根据头部 url 拼接其他页码的url
def all_url_callback(self, response): # 解析并拼接所有需要爬取的 url 地址
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.body, "html5lib")
div = soup.find_all("div", attrs={"id": "rentid_D10_01"}) # 获取各地区的 url 地址的 dl 标签
span = div[0].find_all("span") # 获取 dl 标签中所有的 span 标签,
span_text = span[0].text
for index in range(int(span_text[1:len(span_text) - 1])):
if index == 0:
pass
# self.allUrlList.append(self.baseUrl + my_a["href"])
else:
if self.baseUrl == response.url:
self.allUrlList.append(response.url + "house/i3" + str(index + 1) + "/")
continue
self.allUrlList.append(response.url + "i3" + str(index + 1) + "/")
if len(self.headUrlList) == 0:
url = self.allUrlList.pop(0)
yield Request(url, callback=self.parse, dont_filter=True)
else:
url = self.headUrlList.pop(0)
yield Request(url, callback=self.all_url_callback, dont_filter=True)
最后解析一个页面的数据
def parse(self, response): # 解析一个页面的数据
self.logger.info("==========================")
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.body, "html5lib")
divs = soup.find_all("dd", attrs={"class": "info rel"}) # 获取需要爬取得 div
for div in divs:
ps = div.find_all("p")
try: # 捕获异常,因为页面中有些数据没有被填写完整,或者被插入了一条广告,则会没有相应的标签,所以会报错
for index, p in enumerate(ps): # 从源码中可以看出,每一条 p 标签都有我们想要的信息,故在此遍历 p 标签,
text = p.text.strip()
print(text) # 输出看看是否为我们想要的信息
roomMsg = ps[1].text.split("|")
area = roomMsg[2].strip()[:len(roomMsg[2]) - 1]
item = RenthousescrapyItem()
item["title"] = ps[0].text.strip()
item["rooms"] = roomMsg[1].strip()
item["area"] = int(float(area))
item["price"] = int(ps[len(ps) - 1].text.strip()[:len(ps[len(ps) - 1].text.strip()) - 3])
item["address"] = ps[2].text.strip()
item["traffic"] = ps[3].text.strip()
if (self.baseUrl+"house/") in response.url: # 对不限区域的地方进行区分
item["region"] = "不限"
else:
item["region"] = ps[2].text.strip()[:2]
item["direction"] = roomMsg[3].strip()
print(item)
yield item
except:
print("糟糕,出现 exception")
continue
if len(self.allUrlList) != 0:
url = self.allUrlList.pop(0)
yield Request(url, callback=self.parse, dont_filter=True)
数据分析实现
这里主要通过 pymongo 的一些聚合运算来进行统计,再结合相关的图标库,来进行数据的展示。
数据分析:
# 求一个区的房租单价(平方米/元)
def getAvgPrice(self, region):
areaPinYin = self.getPinyin(region=region)
collection = self.zfdb[areaPinYin]
totalPrice = collection.aggregate([{'$group': {'_id': '$region', 'total_price': {'$sum': '$price'}}}])
totalArea = collection.aggregate([{'$group': {'_id': '$region', 'total_area': {'$sum': '$area'}}}])
totalPrice2 = list(totalPrice)[0]["total_price"]
totalArea2 = list(totalArea)[0]["total_area"]
return totalPrice2 / totalArea2
# 获取各个区 每个月一平方米需要多少钱
def getTotalAvgPrice(self):
totalAvgPriceList = []
totalAvgPriceDirList = []
for index, region in enumerate(self.getAreaList()):
avgPrice = self.getAvgPrice(region)
totalAvgPriceList.append(round(avgPrice, 3))
totalAvgPriceDirList.append({"value": round(avgPrice, 3), "name": region + " " + str(round(avgPrice, 3))})
return totalAvgPriceDirList
# 获取各个区 每一天一平方米需要多少钱
def getTotalAvgPricePerDay(self):
totalAvgPriceList = []
for index, region in enumerate(self.getAreaList()):
avgPrice = self.getAvgPrice(region)
totalAvgPriceList.append(round(avgPrice / 30, 3))
return (self.getAreaList(), totalAvgPriceList)
# 获取各区统计样本数量
def getAnalycisNum(self):
analycisList = []
for index, region in enumerate(self.getAreaList()):
collection = self.zfdb[self.pinyinDir[region]]
print(region)
totalNum = collection.aggregate([{'$group': {'_id': '', 'total_num': {'$sum': 1}}}])
totalNum2 = list(totalNum)[0]["total_num"]
analycisList.append(totalNum2)
return (self.getAreaList(), analycisList)
# 获取各个区的房源比重
def getAreaWeight(self):
result = self.zfdb.rent.aggregate([{'$group': {'_id': '$region', 'weight': {'$sum': 1}}}])
areaName = []
areaWeight = []
for item in result:
if item["_id"] in self.getAreaList():
areaWeight.append(item["weight"])
areaName.append(item["_id"])
print(item["_id"])
print(item["weight"])
# print(type(item))
return (areaName, areaWeight)
# 获取 title 数据,用于构建词云
def getTitle(self):
collection = self.zfdb["rent"]
queryArgs = {}
projectionFields = {'_id': False, 'title': True} # 用字典指定需要的字段
searchRes = collection.find(queryArgs, projection=projectionFields).limit(1000)
content = ''
for result in searchRes:
print(result["title"])
content += result["title"]
return content
# 获取户型数据(例如:3 室 2 厅)
def getRooms(self):
results = self.zfdb.rent.aggregate([{'$group': {'_id': '$rooms', 'weight': {'$sum': 1}}}])
roomList = []
weightList = []
for result in results:
roomList.append(result["_id"])
weightList.append(result["weight"])
# print(list(result))
return (roomList, weightList)
# 获取租房面积
def getAcreage(self):
results0_30 = self.zfdb.rent.aggregate([
{'$match': {'area': {'$gt': 0, '$lte': 30}}},
{'$group': {'_id': '', 'count': {'$sum': 1}}}
])
results30_60 = self.zfdb.rent.aggregate([
{'$match': {'area': {'$gt': 30, '$lte': 60}}},
{'$group': {'_id': '', 'count': {'$sum': 1}}}
])
results60_90 = self.zfdb.rent.aggregate([
{'$match': {'area': {'$gt': 60, '$lte': 90}}},
{'$group': {'_id': '', 'count': {'$sum': 1}}}
])
results90_120 = self.zfdb.rent.aggregate([
{'$match': {'area': {'$gt': 90, '$lte': 120}}},
{'$group': {'_id': '', 'count': {'$sum': 1}}}
])
results120_200 = self.zfdb.rent.aggregate([
{'$match': {'area': {'$gt': 120, '$lte': 200}}},
{'$group': {'_id': '', 'count': {'$sum': 1}}}
])
results200_300 = self.zfdb.rent.aggregate([
{'$match': {'area': {'$gt': 200, '$lte': 300}}},
{'$group': {'_id': '', 'count': {'$sum': 1}}}
])
results300_400 = self.zfdb.rent.aggregate([
{'$match': {'area': {'$gt': 300, '$lte': 400}}},
{'$group': {'_id': '', 'count': {'$sum': 1}}}
])
results400_10000 = self.zfdb.rent.aggregate([
{'$match': {'area': {'$gt': 300, '$lte': 10000}}},
{'$group': {'_id': '', 'count': {'$sum': 1}}}
])
results0_30_ = list(results0_30)[0]["count"]
results30_60_ = list(results30_60)[0]["count"]
results60_90_ = list(results60_90)[0]["count"]
results90_120_ = list(results90_120)[0]["count"]
results120_200_ = list(results120_200)[0]["count"]
results200_300_ = list(results200_300)[0]["count"]
results300_400_ = list(results300_400)[0]["count"]
results400_10000_ = list(results400_10000)[0]["count"]
attr = ["0-30平方米", "30-60平方米", "60-90平方米", "90-120平方米", "120-200平方米", "200-300平方米", "300-400平方米", "400+平方米"]
value = [
results0_30_, results30_60_, results60_90_, results90_120_, results120_200_, results200_300_, results300_400_, results400_10000_
]
return (attr, value)
数据展示:
# 展示饼图
def showPie(self, title, attr, value):
from pyecharts import Pie
pie = Pie(title)
pie.add("aa", attr, value, is_label_show=True)
pie.render()
# 展示矩形树图
def showTreeMap(self, title, data):
from pyecharts import TreeMap
data = data
treemap = TreeMap(title, width=1200, height=600)
treemap.add("深圳", data, is_label_show=True, label_pos='inside', label_text_size=19)
treemap.render()
# 展示条形图
def showLine(self, title, attr, value):
from pyecharts import Bar
bar = Bar(title)
bar.add("深圳", attr, value, is_convert=False, is_label_show=True, label_text_size=18, is_random=True,
# xaxis_interval=0, xaxis_label_textsize=9,
legend_text_size=18, label_text_color=["#000"])
bar.render()
# 展示词云
def showWorkCloud(self, content, image_filename, font_filename, out_filename):
d = path.dirname(__name__)
# content = open(path.join(d, filename), 'rb').read()
# 基于TF-IDF算法的关键字抽取, topK返回频率最高的几项, 默认值为20, withWeight
# 为是否返回关键字的权重
tags = jieba.analyse.extract_tags(content, topK=100, withWeight=False)
text = " ".join(tags)
# 需要显示的背景图片
img = imread(path.join(d, image_filename))
# 指定中文字体, 不然会乱码的
wc = WordCloud(font_path=font_filename,
background_color='black',
# 词云形状,
mask=img,
# 允许最大词汇
max_words=400,
# 最大号字体,如果不指定则为图像高度
max_font_size=100,
# 画布宽度和高度,如果设置了msak则不会生效
# width=600,
# height=400,
margin=2,
# 词语水平摆放的频率,默认为0.9.即竖直摆放的频率为0.1
prefer_horizontal=0.9
)
wc.generate(text)
img_color = ImageColorGenerator(img)
plt.imshow(wc.recolor(color_func=img_color))
plt.axis("off")
plt.show()
wc.to_file(path.join(d, out_filename))
# 展示 pyecharts 的词云
def showPyechartsWordCloud(self, attr, value):
from pyecharts import WordCloud
wordcloud = WordCloud(width=1300, height=620)
wordcloud.add("", attr, value, word_size_range=[20, 100])
wordcloud.render()
后记
距离上一篇租房市场的分析已经3、4 个月了,我的技术水平也得到了一定的提高。所以努力编码才是成长的捷径。最后,应对外界条件的变动,我们还是应该提升自己的硬实力,这样才能提升自己的生存能力。后台回复【广州租房】获取源码。
原创文章,作者:fendouai,如若转载,请注明出处:https://panchuang.net/2019/01/03/b5dcf116c6/

